Trump vs. Harris
Why support Harris
With Biden:
- Chips and Science Act More Info
- Pact Act More Info
- Inflation Reduction Act More Info
- The Bipartisan Infrastructure Bill More Info
- The American Rescue Plan More Info
Ran on:
- $2000 Cap on Pharmaceuticals out of pocket
- $35 Cap on Insulin for EVERYONE, not just people on Medicare
- Expanding the ACA
- Increasing the Federal Minimum Wage
Why not support Trump
- He was held civilly liable for sexually assaulting a woman.
- He bragged about walking into the changing room of underage girls at the miss teen USA pageant without their consent.
- Said he would date a ten year old girl in ten years.
- He sent false slates of electors to the electoral college to cast votes in the 2020 election to try to steal the election.
- He called for the termination of the constitution.
- He incited a violent insurrection at the capitol.
- He pardoned violent rioters on January 6 who beat police officers.
- “Big Beautiful Bill” gives enormous tax breaks to millionaires and billionaires.
- Trump said specifically to big fossil fuel companies that if they gave a billion dollars to his campaign that he would give them 110 billion dollars in tax cuts.
- He signed off on four trillion dollars more in debt related spending under his administration compared to the Biden / Harris administration (according to the Committee for Responsible Budget – non partisan committee from the federal government).
Since Trump took office in 2025
- Real GDP declined for Q1 of 2025.
- Job Growth has decreased.
- Unemployment is increasing (jobs report so bad he fired the head of the bureau of labor statistics).
- Inflation is increasing.
Sources
- AP News
- NPR
- PBS
- Reuters
- Bureau of Labor Statistics
- St. Lewis Federal Reserve
- The Congressional Budget Office
- The Committee for Responsible Federal Budget
Chips and Science Act
What It Is
- Signed into law by President Joe Biden on August 9, 2022, this federal legislation is officially known as the CHIPS and Science Act, enacted by the 117th U.S. Congress WikipediaUnited States Studies Centre.
- It’s one of the largest investments in U.S. manufacturing and research in decades, aiming to strengthen domestic semiconductor production and science capabilities United States Studies CentreMcKinsey & Company.
Investment Breakdown
Total Funding Commitment
- Around $280 billion is authorized over approximately ten years WikipediaMcKinsey & CompanyUnited States Studies Centre.
CHIPS Component (Semiconductor Focus)
- $52.7 billion is directly appropriated for semiconductors, including:
- $39 billion in subsidies, grants, loans, and loan guarantees for U.S.-based chip manufacturing WikipediaU.S. Senator Michael BennetCouncil on Foreign Relations.
- A 25% investment tax credit for semiconductor manufacturing equipment—estimated at $24 billion in tax benefits McKinsey & CompanyWikipediaWikipedia.
- $11 billion allocated for semiconductor research, development, and workforce training—supporting institutions like the National Semiconductor Technology Center and advanced packaging initiatives WikipediaU.S. Senator Michael BennetMcKinsey & Company.
- Additional funds: $2 billion for legacy chip production (for critical industries like automotive and defense), and $200 million to the NSF for workforce development U.S. Senator Michael Bennet.
- Funding for international coordination ($500 million) and defense-related semiconductor prototyping and workforce training ($2 billion) U.S. Senator Michael Bennet.
Science Component (Broader R&D)
- Up to $174 billion is authorized for science and technology R&D, STEM workforce development, and commercialization across federal agencies such as NSF, NASA, DOE, NIST, and EDA WikipediaMcKinsey & CompanyWikipedia.
- A portion—about $80 billion—is earmarked for NSF McKinsey & CompanyWikipedia.
Strategic Rationale
- The law responds to a sharp decline in U.S. chip production—from ~37% of global supply in 1990 to ~12% today—as the U.S. became heavily reliant on foreign sources Council on Foreign RelationsUnited States Studies CentreWIRED.
- Supply chain disruptions during the pandemic and geopolitical competition—especially with China—heightened the urgency to rebuild domestic manufacturing and safeguard national security WikipediaTIMEAP News.
Results and Challenges So Far
- Approval of significant grants and loans: e.g., Intel (
$8.5B in grants, $11B in loans) and TSMC ($6.6B in grants, $5B in loans) to build fabs in the U.S. Council on Foreign Relations. - Hundreds of chip companies have applied, totaling over $70 billion—well above available funds Council on Foreign Relations.
- Private-sector investments have surged—over $200 billion announced since the act’s passage Council on Foreign RelationsWikipedia.
- The goal: increase U.S. share in advanced chip production to ~20% by 2030 Council on Foreign Relations.
Implementation Hurdles
- Delays in facility construction related to labor, materials, and costs McKinsey & CompanyInvestorsCouncil on Foreign Relations.
- Workforce shortages continue to be a critical challenge InvestorsAP News.
- Critics warn that the distribution of funds and complexity of incentives may disproportionately benefit large firms WIREDCouncil on Foreign Relations.
- Some science agencies have subsequently been underfunded compared to the Act’s authorizations, leaving an $8 billion shortfall in key research areas Wikipedia.
Summary Table
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Rebuild U.S. semiconductor production, secure supply chains, invest in STEM innovation |
| Total Authorized | ≈ $280 billion |
| Semiconductors | $52.7B appropriated: grants, loans, tax credits, R&D, workforce |
| Science | $174B authorized across agencies |
| Key Goals | Increase chip manufacturing, support advanced tech, diversify STEM workforce |
| Current Issues | Project delays, funding shortfalls, workforce gaps, distribution critique |
Pact Act
Overview & Legislative History
- The formal name of the law is the Sergeant First Class Heath Robinson Honoring our Promise to Address Comprehensive Toxics Act of 2022, commonly referred to as the PACT Act Wikipedia.
- Introduced in the U.S. House on June 17, 2021 by Rep. Mark Takano. It passed both chambers with bipartisan support in 2022, and was signed into law by President Joe Biden on August 10, 2022, going into effect immediately WikipediaDAVThe White House.
Key Provisions & Impact
1. Expanded VA Eligibility & Health Care Access
- The most significant expansion of VA health care and benefits for toxic-exposed veterans in over 30 years The White HouseDAV.
- It expands VA health care eligibility for veterans from:
- Vietnam, Gulf War, and Post-9/11 eras,
- with combat veterans now having 10 years (instead of 5) post-discharge to enroll, and others receiving a one-year open enrollment window DAVThe White HouseVeterans Affairs.
- Starting March 5, 2024, millions of veterans could access VA health care immediately, without needing to apply for benefits first—ahead of the full phase-in Business Insider.
2. Presumptive Conditions for Toxic Exposure
- Over 20 new “presumptive” conditions added, meaning veterans no longer must prove their illness is connected to their service. These include:
- Numerous respiratory illnesses: asthma (post-service), chronic bronchitis, COPD, chronic rhinitis/sinusitis, constrictive bronchiolitis, emphysema, interstitial lung disease, pleuritis, pulmonary fibrosis, sarcoidosis Public Health VAVA Claims Insider.
- Various cancers: brain, gastrointestinal, head, neck, kidney, lymphatic, lymphoma, melanoma, pancreatic, reproductive, and respiratory cancers Public Health VAVA Claims Insider.
- Expansion of Agent Orange and radiation presumptions, now including service in Thailand, Cambodia, Laos, Guam, American Samoa, Johnston Atoll, and additional locations DAVlawshun.com.
- Toxic exposure screenings are now required for every veteran enrolled in VA health care, with follow-up screenings at least every five years Veterans Affairs+1.
3. Research, Training & Infrastructure
- Mandates new studies into veterans’ health trends (e.g. Gulf War, post-9/11, cancer rates) and establishes a five-year strategic plan for toxic exposure research The White HouseVeterans Affairs.
- Requires training for VA personnel and increased outreach related to toxic exposure benefits The White HouseVeterans Affairs.
- Authorizes expansion of the VA workforce and building of up to 31 new major medical clinics and research facilities across 19 states The White HouseVeterans Affairs.
4. Camp Lejeune Justice Act
- Incorporated as Section 804, granting new legal avenues for veterans and others harmed by toxic water exposure at Camp Lejeune (1953–1987), enabling lawsuits previously blocked under the Federal Tort Claims Act WikipediaTIME.
Outcomes & Implementation (as of 2024)
- Since enactment, the VA has processed over 1.5 million PACT Act–related claims, delivering benefits to over 1 million veterans and 10,000+ survivors, totaling more than $6.8 billion The White HouseAP News.
- Enrollment in VA health care increased by 33%, with over 739,000 new enrollees including more than 333,000 veterans specifically from eligible eras The White House.
- Prior to the law, approximately 70–78% of burn pit–related claims were denied. The PACT Act reversed that trend by establishing presumptive service connection for numerous conditions, significantly streamlining the claims process WikipediaAP NewsDAV.
Summary Table
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Enactment | Signed into law on August 10, 2022 |
| Scope | Largest VA benefit expansion in 30+ years |
| VA Health Access | Expanded eligibility; extended enrollment windows; earlier access since March 2024 |
| Presumptive Conditions | 20+ respiratory illnesses & 11 cancer categories now presumptive |
| Agent Orange Locations | Expanded to additional countries/regions |
| Screening & Training | Mandatory toxic exposure screenings; VA staff training & outreach |
| Research & Facilities | New studies; strategic plan; 31 new health and research clinics |
| Camp Lejeune Claims | New tort claims allowed for toxic water exposure |
| Results | Over 1 million veterans/survivors helped; $6.8B distributed; claim processing record highs |
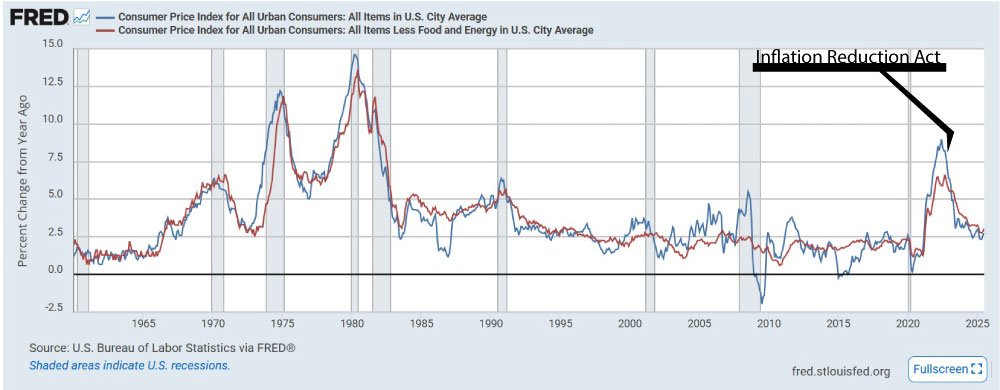
Inflation Reduction Act
What Is It & When It Passed
- The Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 (IRA) is landmark U.S. legislation passed by the 117th Congress and signed into law by President Biden on August 16, 2022 WikipediaVogue.
- It emerged as a scaled-down, post-“Build Back Better” package, reshaped through bipartisan negotiations led by Senators Schumer and Manchin WikipediaMcKinsey & Company.
Core Objectives
- Reduce the Budget Deficit
- Lower Healthcare and Prescription Costs
- Invest in Clean Energy & Fight Climate Change
- Boost Tax Fairness and Fund IRS Modernization
WikipediaMcKinsey & CompanyFederal Reserve Bank of RichmondThe White House
Key Provisions & Allocations
Healthcare & Prescription Costs
- Allows Medicare to negotiate drug prices; rebates for price hikes above inflation WikipediaIndivisiblehealthinsurance.org.
- Caps insulin at $35/month (effective 2023 for Part D; mid-2023 for Part B) healthinsurance.orgWikipedia.
- Limits out-of-pocket prescription costs to $2,000/year (starting 2025) healthinsurance.orgIndivisibleSchwab Brokerage.
- Extends Affordable Care Act (ACA) marketplace subsidies through 2025, saving consumers ~$800/year Schwab BrokerageCenter for American ProgressThe White House.
Clean Energy & Climate Action
- Nearly $400 billion allocated for clean energy and climate investments over 10 years McKinsey & CompanyIndivisibleEarth.Org.
- Tax credits and incentives for:
- Home energy upgrades (heat pumps, insulation, solar, etc.)—typically 30% of cost, often with caps The Department of Energy’s Energy.govRamsey SolutionsPBS.
- Electric vehicle (EV) purchases—up to $7,500 for new, $4,000 for used vehicles McKinsey & CompanyIndivisibleSchwab Brokerage.
- Carbon capture & sequestration technologies, with enhanced per-ton incentives Earth.Org.
- Investments in clean tech manufacturing, grid infrastructure, climate resilience, agriculture, environmental justice, and more WikipediaIndivisibleCenter for American ProgressMcKinsey & Company.
Tax, Revenue & IRS Modernization
- 15% corporate minimum tax on firms earning over $1B/year WikipediaPBSThe White House.
- 1% excise tax on stock buybacks WikipediaPBSThe White House.
- ~$80 billion funding for IRS modernization, enforcement, and staffing WikipediaSchwab BrokerageThe White House.
Fiscal Impacts & Deficit Reduction
- The Congressional Budget Office (CBO) estimated the Act would reduce the federal deficit by ~$237 billion over 10 years McKinsey & CompanyFederal Reserve Bank of RichmondCenter for American Progress.
- McKinsey-style summaries affirm that clean energy investments will be delivered via a mix of tax credits, grants, and loans, with clean energy and manufacturing being primary beneficiaries McKinsey & CompanyIndivisibleCenter for American Progress.
Projected Benefits
- Energy Savings: Households could save $200–$1,000+ annually on energy costs, with some states seeing larger impacts Center for American ProgressThe Department of Energy’s Energy.gov.
- Medical Savings: Millions of Medicare beneficiaries will benefit from drug cost caps, insulin reduction, and negotiated prices The White HouseCenter for American Progresshealthinsurance.org.
- Job & Economic Growth: Boosted domestic manufacturing, job creation in clean energy sectors, and climate-resilient infrastructure investments IndivisibleMcKinsey & CompanyThe Department of Energy’s Energy.gov.
Summary Table
| Category | Highlights |
|---|---|
| Date Enacted | August 16, 2022 |
| Total Scale | Approx. $750B package |
| Healthcare | Drug negotiation, insulin & prescription caps, ACA subsidies extension |
| Clean Energy | ~ $400B investment in energy, EVs, efficiency, carbon capture |
| Taxes & IRS | 15% corporate minimum, 1% buyback tax, $80B for IRS modernization |
| Deficit Impact | ~$237B reduction over 10 years |
| Benefits | Lower energy bills, healthcare cost relief, jobs, climate resilience |
Bipartisan Infrastructure Bill
Here’s a clear and up-to-date summary of the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law (formally the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act, enacted November 15, 2021):
What It Is & When It Became Law
- The Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA), also widely known as the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, was signed into law by President Biden on November 15, 2021, after receiving support from both parties in Congress. AxiosCongress.gov
- It authorized a total of approximately $1.2 trillion in spending, including about $550 billion in brand-new investments targeting critical infrastructure. Government Finance Officers Association
Key Investment Areas & Funding Allocations
Here’s how the investments break down across major sectors: Wikipedia+1Brookings
- Roads, Bridges & Major Projects — ~$110 billion
- Transportation Safety Programs — ~$11 billion
- Public Transit Modernization — ~$39 billion
- Passenger & Freight Rail — ~$66 billion
- Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Infrastructure — ~$7.5 billion (via NEVI program)
- Power Infrastructure & Clean Energy Transmission — ~$73 billion
- Broadband Expansion — ~$65 billion
- Additional funding includes airports, ports and waterways, water systems, ecosystem resilience, dams, and more. WikipediaCongress.govBrookings
Water Infrastructure, Climate & Equity
- Water & Environmental Infrastructure:
- $11.7B for Drinking Water State Revolving Fund
- $15B to replace lead service lines
- $9B to address PFAS and emerging contaminants
- Clean Water SRF funding, Western water infrastructure, and support for rural and tribal communities also included. Wikipedia
- Climate Resilience & Environmental Priorities:
- Wildlife crossings pilot program — $350M
- Culvert removal and habitat restoration — $1B
- Reconnecting Communities to cap or remove highways in marginalized areas — $1B
- Ecosystem restoration and clean school buses are other featured benefits. WikipediaBusiness Insider
Progress & Impact (as of 2024–2025)
- Nearly $570 billion in BIL funding has been announced across 66,000+ projects nationwide, covering roads, bridges, ports, airports, tribal lands, and more. Department of Transportation
- Roadwork spans over 196,000 miles
- Bridge upgrades include 11,400+ projects
- 580+ port and waterway initiatives underway
- 1,500+ airports modernizing terminals or runways Department of Transportation
- High-profile infrastructure projects benefiting from the law include:
- Replacement of the John A. Blatnik Bridge (MN–WI) with $1.06B in funding
- Replacing the Interstate Bridge between Portland, OR, and Vancouver, WA — awarded over $2B from federal programs Business Insider
Economic Outcomes & Long-Term Benefits
- This landmark investment is estimated to create hundreds of thousands of jobs annually:
- ~772,000 jobs per year supported overall
- ~196,000 road and bridge jobs, ~23,000 port jobs, ~26,000 airport jobs
- ~60,000 broadband-related roles, ~70,000 in public transit, ~80,000 in water upgrades, and ~89,000 in climate resilience infrastructure Joint Economic Committee
- Economists and experts say the law will help reduce long-term inflation by improving supply chains and boosting productivity. Infrastructure investments have shown returns of up to 17%. Joint Economic Committee
Quick Summary Table
| Area | Description |
|---|---|
| Enacted | November 15, 2021 |
| Total Funding | ~$1.2 trillion (including ~$550B new spending) |
| Major Categories | Roads, Bridges, Transit, Rail, EV Infrastructure, Energy, Broadband, Water Quality, Climate Resilience |
| Current Status | $570B+ in announcements across 66,000+ projects |
| Economic Benefits | Hundreds of thousands of jobs annually; boost to supply chain resilience and productivity |
The American Rescue Plan
What It Is & When It Passed
- The American Rescue Plan Act of 2021, commonly known as ARPA, is a $1.9 trillion federal relief package signed into law by President Biden on March 11, 2021 Wikipediapandemicoversight.gov.
- It was the second-largest pandemic-era stimulus after the CARES Act and aimed to provide economic relief, public health funding, and recovery support across multiple sectors pandemicoversight.govWikipedia.
- Economists estimate it cut the adult poverty rate by 25% and child poverty by 50% Wikipedia.
Major Components & Provisions
1. Direct Financial Relief to Individuals & Families
- Third-round stimulus checks of up to $1,400 per person, plus $1,400 per dependent; phased out above certain income thresholds (e.g., $75,000 individual; $150,000 joint) Chortekvintti.comWikipedia.
- Expanded Child Tax Credit for 2021: up to $3,600 per child under 6, and $3,000 for ages 6–17; fully refundable; delivered via monthly payments from July–December 2021 Wikipedia+1vintti.com.
- Child and Dependent Care Credit enhanced: refundability increased, up to $4,000 credit for one dependent and $8,000 for two or more WikipediaSequoia Financial Group –.
2. Unemployment & Job Support
- Extended $300 weekly federal unemployment benefit through September 6, 2021 ChortekMeadows UrquhartThomson Reuters Legal.
- Made the first $10,200 of 2020 unemployment benefits tax-free for households under certain income thresholds ChortekSequoia Financial Group –.
3. Business and Nonprofit Support
- Boosted the Employee Retention Tax Credit (ERTC) through end of 2021, inclusive of employers that began operations after early 2020 Meadows Urquharthrserviceinc.com.
- Injected additional Paycheck Protection Program (PPP) funds, expanded eligibility to more nonprofits Meadows Urquhart.
- Created a Restaurant Revitalization Fund and grants for entertainment venues impacted by the pandemic vintti.comMeadows Urquhart.
4. Healthcare & Public Health
- Allocated substantial funding for COVID vaccines, testing, tracing, and mitigation, including $50B to FEMA, $47.8B for testing and tracing, and billions for vaccine distribution, health centers, and data systems Wikipedia.
- COBRA premium subsidy: employers could claim credit to cover COBRA premiums for furloughed workers April–September 2021 vintti.comSequoia Financial Group –.
- Enhanced ACA premium tax credits, eliminated income cap for 2021 and 2022, and lowered premium shares—this widened eligibility and reduced costs through the market ChortekVerywell HealthInvestopedia.
- Additional funding for behavioral health: mental health block grants, substance abuse programs, workforce training, and mobile crisis services in Medicaid American Hospital Association.
5. State, Local & Tribal Government Aid
- Provided $350 billion in fiscal relief: ~$219.8B to states, $130B to cities/counties, and dedicated funds for territories and tribal governments Akin – Akin, an Elite Global Law FirmHolland & KnightArmanino LLP.
- Funds could be used for public health, revenue replacement, premium pay, and infrastructure like water and broadband Akin – Akin, an Elite Global Law Firm.
6. Education & Connectivity
- Launched ESSER 3.0: emergency aid to K–12 schools, bolstering reopening and mitigation efforts Wikipedia.
- Created a $7.2 billion Emergency Connectivity Fund to help schools and libraries provide internet access and devices to students NCSLpandemicoversight.gov.
7. Oversight & Anti-Fraud
- Established the American Rescue Plan Implementation Team, weekly oversight meetings, and invested $40 million into analytics to detect fraud; resulted in hundreds of fraud indictments and protections pandemicoversight.gov.
8. Pension Relief
- Provided a bailout for multiemployer pension plans (Butch Lewis Act), protecting benefits for millions, including workers in Wisconsin WikipediaReddit.
Summary Table
| Category | Key Highlights |
|---|---|
| Relief Amount | Total ~$1.9 trillion |
| Direct Payments | $1,400 per individual/dependent |
| Child Tax Credit | Up to $3,600/3,000 per child, with monthly payments |
| Unemployment Relief | $300/week + first $10,200 tax-free |
| Business Support | PPP, ERTC, grants for restaurants/venues |
| Healthcare | Vaccine/testing funding; COBRA subsidies; ACA subsidy enhancements |
| Mental Health | Block grants, workforce training, mobile crisis funding |
| Government Aid | $350B to states, cities, tribes; infrastructure uses |
| Education Support | ESSER 3.0 and device/internet connectivity fund |
| Oversight | Fraud detection and implementation oversight |
| Pension Protection | Multiemployer pension plan relief (Butch Lewis Act) |
Impact & Outcomes
- ACA marketplace enrollment soared due to enhanced subsidies—many saved $33–$213/month on premiums, with an average drop of ~$50/person/month InvestopediaVerywell Health.
- Pension plans on the brink of collapse were stabilized, preserving benefits for workers and retirees Reddit.
- Delivered record-breaking fiscal resilience for local governments and schools, and strengthened broadband and public health infrastructure.